Wheat Diseases
There are a variety of diseases that attack wheat in northwest Kansas. Some of these can be prevented and some can be treated. They affect the roots, leaves and heads of the wheat plants. Some of the most common diseases are wheat streak mosaic (virus), stripe rust (fungus), and root and crown rot (fungus).
Foliar Fungicide Efficacy Ratings.
Evaluating the Need for Wheat Foliar Fungicides. Order the print version of this publication
Wheat Variety Guide for 2023 (includes disease and insect ratings)
Frequently Asked Questions on current wheat fungicide use issues
Stripe rust continues to be a serious concern for many wheat growers in the state. The threat of yield losses to stripe rust has many growers looking into fungicide options. Here are some common questions that others are asking about wheat fungicides and their use.
Q: Are generic fungicides as effective as the more expensive products?
A: In tests conducted by universities throughout the Central Plains and Midwest in recent years, researchers have found no significant differences in the efficacy of products with identical active ingredients. In other words, the generic fungicides are equally effective when used at the same rates as other products with the same active ingredient. We provide an efficacy rating of fungicide products in Foliar Fungicide Efficacy Ratings for Wheat Disease Management 2016, K-State Research and Extension publication EP-130: http://www.bookstore.ksre.ksu.edu/pubs/EP130.pdf
In this publication, you can compare the efficacy ratings of many different products (including products that contain more than one mode of action) for stripe rust and many common wheat diseases. In general, wheat growers have many very good or excellent product options. In my experience, correctly identifying when a fungicide is needed and timeliness of the application are more important than which product is being used in most cases. Control of Fusarium head blight (scab) is the exception. For Fusarium head blight control, triazole fungicides are the best option. This includes products such as Prosaro, Caramba, and Folicur (or generic tebuconazole). See the fungicide efficacy publication mentioned above for more information.
Q: Are there other issues to consider when selecting a product?
A: Yes. There is a growing concern about fungicide resistance in some parts of the country. For a long time, those of us growing field crops didn’t really have to worry much about this issue, but that is no longer the case. The development of fungicide resistance can be slowed by alternating modes of action between years, by using a product that contains multiple modes of action, or tank-mixing different modes of action. Products containing only strobilurin fungicides are most at risk for fungicide resistance.
Another factor to consider is the maximum amount of any one active ingredient that can be used per season. If an early application of tebuconazole is made, for example, you will not be able to apply the full rate of a product now if that product would put you over the limit for tebuconazole for the season. This is one of the potential downside risks of making an early-season application of a fungicide.
Q: What is the difference between a “curative” and “preventive” fungicide?
A: Honestly, I don’t really like to use these terms to describe fungicides because I think they can lead people down a confusing path. All fungicides are best applied before the disease becomes established or very early in the development of disease within crop. So from this perspective, all fungicides work best in preventive mode. The triazole fungicides are generally considered to have some limited curative activity but they cannot restore leaf tissue already damaged by the disease. It would be a mistake to think that a fungicide with curative activity does not provide any preventive activity. The different fungicides just stop the infection at slightly different times in the infection process.
Q: Is it best to use a product that combines a multiple modes of action?
A: Growers have a lot of product options with very good or excellent efficacy on stripe rust and other leaf diseases. I suggest that growers consider efficacy ratings, cost, and availability when selecting products to use on their farm. As mentioned previously, using a fungicide with a mixed mode of action can help reduce the risk of fungicide resistance. However, there are other ways to achieve similar results with respect to resistance.
Q: Which fungicides can be applied latest in the season on wheat?
A: Always consult the label on this since any label violations could have unwelcome consequences. In general, the triazole fungicides can be applied the latest. Tebuconazole products (Folicur and generic products), Caramba, and Prosaro can be applied through the flowering stage. But these products have a 30-day preharvest interval as well, so producers have to keep that in mind and make sure they’re not applying it so late that they will have to delay harvest to meet the preharvest interval. Other fungicides have a growth stage cut off that prevents application during and after the flowering stages of growth.
Erick DeWolf, Extension Plant Pathology
dewolf1@ksu.edu
From K-State Extension Agronomy eUpdate 4-22-16
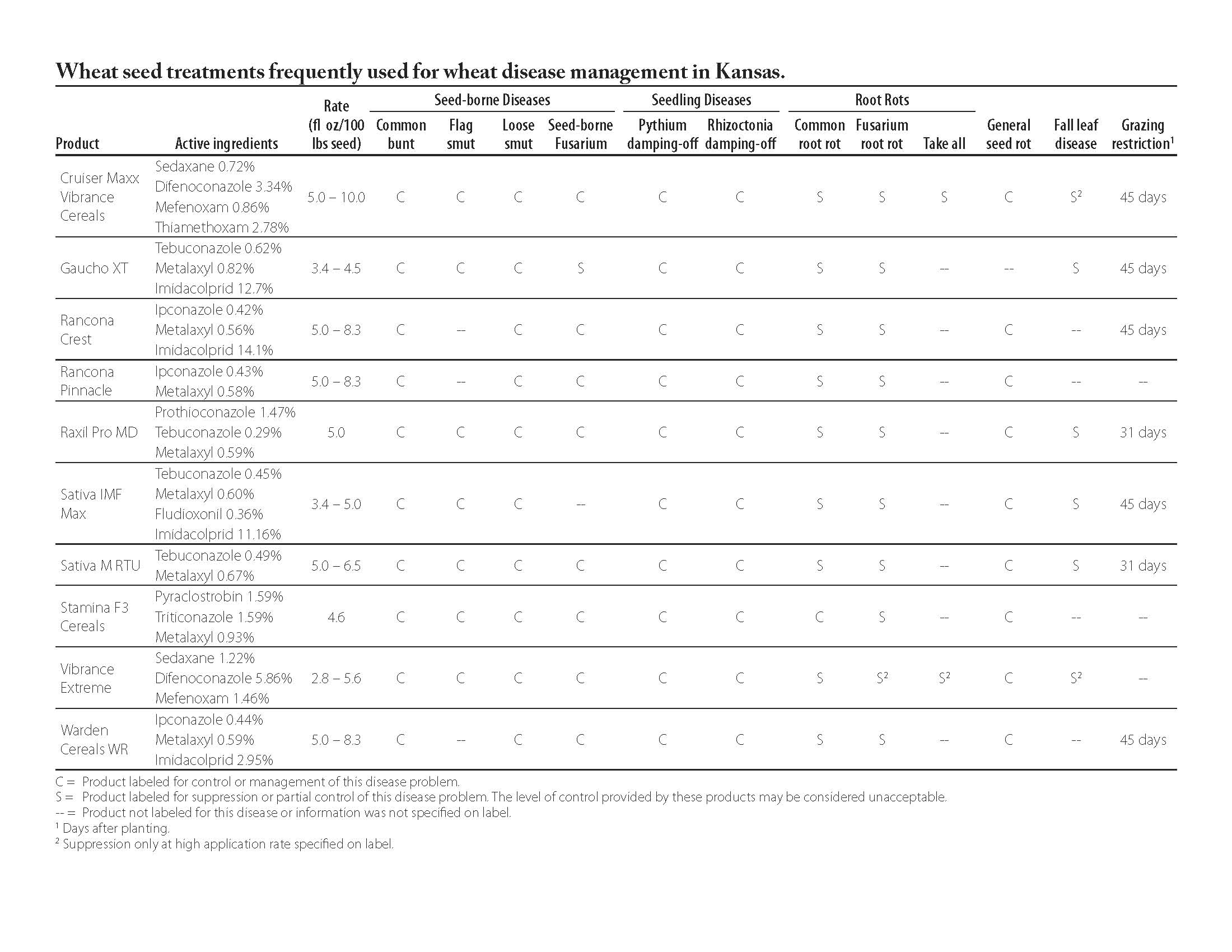
Seed Treatment Fungicides for Wheat Disease Management 2015
Click here for a printable version.